(For his crucial role in negotiations between the West and Russia - Chinese President Hu Jintao would be awarded with Nobel Peace Prize in 2008)
Amidst the tensions that engulfed the Middle East, the Russian government found itself at a critical juncture, carefully considering the implications of international efforts spearheaded by China for diplomatic negotiations between Israel and Syria. With the specter of conflict looming ominously over the region, the opportunity for dialogue presented by these diplomatic overtures was met with a measured but resolute response from Moscow. Understanding the gravity of the situation, the Russian government adopted a stance of cautious optimism, recognizing the potential of diplomatic negotiations to deescalate the Israel-Syria standoff. The commitment to deescalation and the avoidance of further provocations or aggressive actions was embraced wholeheartedly by Moscow, aligning with its broader objective of promoting stability and peace in the region. Central to Russia's response was a reaffirmation of its unwavering commitment to Syrian security. Acknowledging the complex geopolitical landscape in which Syria found itself, the Russian government pledged its support to assist Syria in modernizing its security services and military capabilities. This assistance was seen not only as a means to bolster Syria's defense capabilities but also as a proactive measure to prevent future incursions and maintain the nation's sovereignty. Furthermore, the Russian government signaled its willingness to actively participate in the deescalation process by agreeing to retreat its military forces from the region to precrisis deployment levels. However, this commitment was contingent upon a reciprocal action from the United States, emphasizing the importance of a balanced and synchronized approach to easing tensions. In advocating for deescalation, Moscow called upon both Israel and Syria to cease all mobilization efforts at their respective borders and to retreat their forces. This mutual step back from the brink of conflict was viewed as essential in creating a conducive environment for dialogue and negotiation. Moreover, the Russian government suggested that such a gesture could pave the way for the potential deployment of UN peace troops to the borders, serving as a tangible demonstration of the international community's commitment to stability and security in the region.
In the face of escalating tensions between Turkey and Syria with Russia on the other side, the Russian government adopted a measured and strategic approach aimed at deescalating the standoff while safeguarding its interests in the region. With the specter of conflict looming over the Eastern Mediterranean, Moscow sought to maintain the delicate balance of power while advocating for a return to stability and adherence to established international agreements. Central to Russia's response was the maintenance of its military presence in strategic regions such as the Caucasus and Bulgaria. These deployments served as a deterrent against any further escalation by Turkey and underscored Moscow's commitment to protecting its interests and allies. The decision to keep troops stationed in these areas was contingent upon Turkey's compliance with international norms, particularly the Montreux Convention regarding the passage of ships through the Turkish Straits. By linking troop movements to Turkey's adherence to the convention, Russia signaled its readiness to engage in diplomatic negotiations while also demonstrating its resolve to uphold established legal frameworks.
Moreover, Moscow emphasized its preference for a return to the status quo ante, wherein neither side gained nor lost significant ground. This approach reflected Russia's pragmatic assessment of the situation, recognizing the importance of maintaining stability in the region without seeking to achieve unilateral gains. By advocating for a return to the precrisis levels of military deployment, Russia aimed to deescalate tensions and create space for dialogue and negotiation between the involved parties. At the same time, the Russian government highlighted the need for a resolution to the Syrian nuclear issue involving the United States and Israel. Moscow called for a swift and peaceful resolution to this matter, emphasizing the importance of deescalating tensions in Syria and preventing further exacerbation of the crisis. As part of this resolution, Russia reaffirmed its commitment to Syria's security and development, offering support for the country's modernization efforts. In addressing Turkey's role in the standoff, Russia adopted a diplomatic tone, urging Ankara to return to alignment with international norms and agreements. This included a call for Turkey to demobilize its troops and adhere to the Montreux Convention, thus removing one of the major sources of tension in the region. By engaging with Turkey in a diplomatic manner and emphasizing mutual interests in maintaining stability, Russia sought to deescalate tensions and pave the way for a return to normalcy in the Eastern Mediterranean.
The Russian government acknowledged the importance of the de-escalation approach in the past standoff, recognizing that the outbreak of World War III would have been detrimental to all parties involved. However, it also saw an opportunity to address the underlying issues and perceptions that had contributed to the escalation of tensions, particularly regarding the actions of the United States. First and foremost, Russia aimed to ensure that the U.S. and its constituents understood the sequence of events that had led to the crisis. This included highlighting the fact that the U.S. had approved the initial strike on Syria without exhausting diplomatic channels and condemned Syria for its response. By framing the narrative in this manner, Russia sought to shift the blame for the escalation onto the U.S. and portray itself as a rational actor responding to provocations rather than instigating conflict. Furthermore, Russia aimed to draw attention to what it perceived as a pattern of hostile behavior from the U.S. towards the Union. This included instances where the U.S. had threatened Union allies and then condemned the Union for its responses. By highlighting these incidents, Russia aimed to undermine the credibility of the U.S. and portray it as an aggressor rather than a defender of peace and stability. To effectively convey this message, Russia utilized its international media outlets, such as RT, to spread propaganda and news that aligned with the Union's viewpoint. This included arranging interviews with pro-Union celebrities and influential Russians to amplify the message and reach a wider audience. Through these efforts, Russia aimed to shape public opinion and garner support for its stance on the crisis, portraying itself as a victim of U.S. aggression rather than a perpetrator of conflict.
In response to Moscow's call for de-escalation, the United States, NATO, and Israel carefully weighed their options, considering the implications of the proposed actions against their own strategic interests and security concerns. The United States, cognizant of the risks associated with further escalation and the potential for a wider conflict, ultimately accepted Moscow's proposal for de-escalation. Recognizing the importance of diplomatic efforts in resolving the crisis, the U.S. government agreed to participate in talks aimed at reducing tensions and easing the military buildup in the region. Moreover, Washington saw Moscow's decision to rein in Assad and initiate the demobilization of Syrian troops at the border with Israel as a positive step toward building trust and fostering a conducive environment for dialogue. Similarly, NATO, under the leadership of its member states, endorsed the call for de-escalation and supported the partial demobilization of NATO troops in Europe and the Middle East. Understanding the gravity of the situation and the need to avoid further provocation, NATO welcomed Moscow's efforts to defuse tensions and expressed its commitment to working towards a peaceful resolution to the crisis. As part of this commitment, NATO agreed to reduce its military presence in the region, signaling its willingness to engage in good-faith negotiations aimed at achieving stability and security. However, Israel's response to Russia's proposal for de-escalation was more nuanced. While Israel acknowledged the importance of reducing tensions and avoiding conflict, it remained cautious about the prospect of withdrawing its forces from the border with Syria. Given the complex security dynamics in the region and the ongoing threat posed by hostile actors, including Hezbollah and Iran, Israel expressed reservations about fully embracing the demobilization efforts.
Despite Israel's initial hesitancy, the United States exerted pressure on its ally to align with the broader objectives of de-escalation and partial demobilization. Recognizing the importance of maintaining unity among Western allies and supporting diplomatic initiatives, the U.S. leveraged its influence to persuade Israel to cooperate with the proposed measures. Through diplomatic channels and strategic dialogue, Washington underscored the significance of collective action in averting a potential crisis and preserving regional stability. Following days of intense diplomatic negotiations between the United States, NATO, and Russia, a significant breakthrough was achieved, bringing an end to the crisis that had gripped the international community with fear and uncertainty. The tireless efforts of all parties involved, coupled with the spirit of cooperation and compromise, played a crucial role in de-escalating tensions and restoring stability to the region. At the negotiating table, representatives from the United States, NATO, and Russia engaged in constructive dialogue aimed at addressing the underlying causes of the crisis and finding mutually acceptable solutions. Guided by a shared commitment to peace and security, the negotiators navigated complex geopolitical dynamics with patience, pragmatism, and determination. Key points of contention were addressed through frank and open discussions, with each side demonstrating a willingness to listen to the concerns and perspectives of the others. Recognizing the importance of mutual trust and confidence-building measures, concrete steps were taken to de-escalate the situation and prevent further military confrontation.
As a result of the negotiations, both NATO and Russian troops agreed to return to their respective home bases, easing tensions along the borders and reducing the risk of inadvertent conflict. This significant de-escalation measure was met with relief and cautious optimism by the international community, signaling a renewed commitment to dialogue and diplomacy in resolving disputes. One of the most significant outcomes of the negotiations was Turkey's decision to reopen the Turkish Straits to the Russian Black Sea fleet. The decision by Turkey to reopen the Turkish Straits to the Russian Black Sea fleet was a watershed moment in the resolution of the crisis, albeit one made under considerable pressure from the United States and Western Europe. Ankara's initial reluctance to take this step underscored the complexities and tensions inherent in the geopolitical landscape of the region. However, faced with mounting diplomatic pressure and the prospect of further escalation, Turkey ultimately acquiesced, recognizing the importance of de-escalating the situation and restoring stability to the region. For Russia, the reopening of the Turkish Straits represented a crucial step in easing tensions and reducing the risk of military confrontation. It provided Russian naval forces with vital access to the Mediterranean, enhancing Russia's ability to project power and protect its interests in the region.
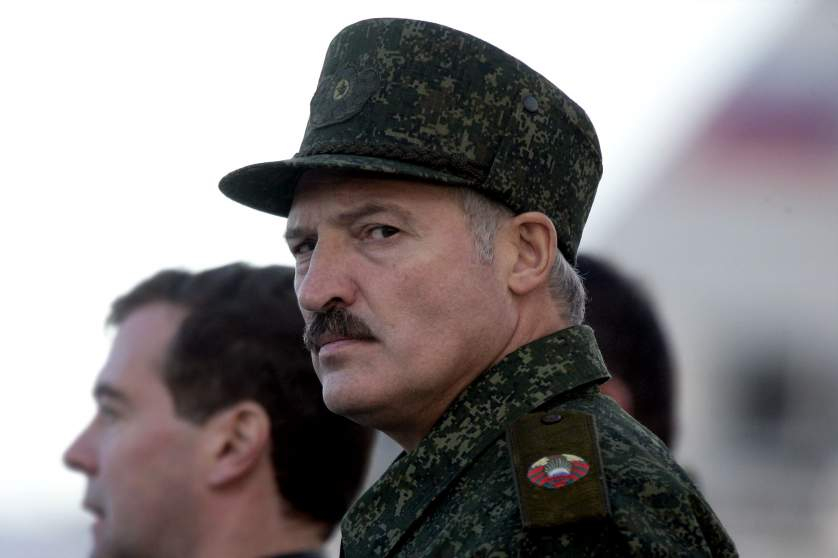

(The outcome of crisis in September 2007 solidified perception of Lukashenko as a strongman both in Russia and rest of the world)
The aftermath of the crisis saw President Lukashenko emerging as a formidable figure on the global stage, bolstering his image as a strongman who was willing to confront the West and defend Russian interests worldwide. The handling of the crisis solidified Lukashenko's reputation as a decisive leader who was unafraid to take bold actions in defense of his country's sovereignty and security. Lukashenko's steadfastness in the face of mounting pressure from the West resonated deeply with the Russian populace, sparking a wave of nationalist fervor and rallying support behind his leadership. His resolute stance against external threats and his unwavering commitment to safeguarding Russian interests garnered widespread admiration and praise from both the public and political elites alike. The crisis served as a defining moment for Lukashenko's presidency, elevating him to a position of greater prominence and influence on the global stage. His deft handling of the situation earned him accolades as a statesman capable of navigating the complexities of international politics with skill and determination. Furthermore, Lukashenko's popularity soared to new heights in the aftermath of the crisis, as the Russian people rallied behind their president in solidarity against perceived Western aggression. His unwavering defense of Russian interests resonated deeply with nationalist sentiments, leading to a surge in support for his leadership and policies. The narrative of Lukashenko as a strong and assertive leader who stood up to Western pressure became deeply entrenched in the public consciousness, shaping perceptions of his presidency for years to come. His ability to project strength and resolve in the face of adversity cemented his status as a symbol of Russian resilience and defiance against external threats. In the wake of the crisis, Lukashenko's government capitalized on his newfound popularity to pursue a more assertive foreign policy agenda, aimed at safeguarding Russian interests and countering Western influence. This included efforts to strengthen alliances with like-minded nations and expand Russia's presence on the global stage. Overall, the aftermath of the crisis saw President Lukashenko emerging as a dominant figure in Russian politics, with his leadership style and nationalist rhetoric resonating strongly with the populace. As Russia sought to assert its position on the world stage, Lukashenko's leadership proved indispensable in guiding the country through turbulent times and shaping its future trajectory.
In the wake of the crisis and the near escalation to a global conflict, criticism of Israel's unilateral actions against Syria reverberated across Europe and the United States, igniting a fervent debate on the international stage. Many voices within these regions condemned Israel's aggressive maneuvers, which were perceived as dangerously provocative and reckless, risking the stability of the entire Middle East and beyond. In Europe, where concerns over the specter of war loomed large, political leaders and public figures expressed deep unease over Israel's actions and their potential ramifications. Calls for restraint and adherence to international norms and laws echoed through the corridors of power, with some European nations openly questioning the legality and morality of Israel's military incursions into Syrian territory. Furthermore, public opinion in Europe was sharply divided, with many citizens expressing outrage and condemnation of Israel's perceived aggression. Protests erupted in major cities, drawing thousands of demonstrators who called for an immediate cessation of hostilities and a return to diplomacy as the preferred means of resolving conflicts in the region. Similarly, in the United States, Israel's actions came under intense scrutiny and criticism from both political leaders and the general public. While Israel's traditional allies in Washington reaffirmed their support for its security and sovereignty, there was a growing chorus of voices questioning the wisdom and prudence of its military intervention in Syria.
Prominent lawmakers and commentators raised concerns about the potential consequences of Israel's actions, warning of the dangers of escalation and the need for restraint in the pursuit of national security objectives. Calls for accountability and transparency in Israeli decision-making processes gained traction, as questions were raised about the legality and justification of its military operations. In the media, coverage of the crisis sparked heated debates and discussions, with pundits and analysts offering a wide range of perspectives on Israel's role in the escalation of tensions in the Middle East. Op-eds and editorials called for a reevaluation of Israel's foreign policy approach and a renewed emphasis on dialogue and diplomacy as the preferred means of resolving regional disputes. Overall, the crisis served as a wake-up call for many in Europe and the United States, prompting a critical reassessment of Israel's actions and their broader implications for global stability and security. As the dust settled and diplomatic efforts to deescalate the situation gained momentum, the international community remained vigilant, wary of the potential for further flare-ups and the need for continued engagement to prevent future crises of similar magnitude.
In September 2007, President George W. Bush faced a precarious political landscape marked by dwindling approval ratings and mounting criticism of his foreign policy decisions. As the leader of the United States, Bush found himself navigating turbulent waters, with his second term characterized by a series of challenges and setbacks that culminated in the recent crisis in the Middle East. Throughout his presidency, Bush's approval ratings had experienced a steady decline, reflecting widespread disillusionment with his administration's handling of key issues both domestically and internationally. The fallout from the Iraq War, which had dragged on for years with no clear end in sight, weighed heavily on public perception of Bush's leadership and competence. The failure to find weapons of mass destruction, the primary justification for the invasion of Iraq, had undermined the credibility of the administration and fueled accusations of deceit and mismanagement. Moreover, the handling of the war on terror, including controversial policies such as the use of enhanced interrogation techniques and the operation of the Guantanamo Bay detention camp, had drawn condemnation from civil liberties advocates and human rights organizations. The erosion of civil liberties in the name of national security had sparked widespread concern and criticism, tarnishing America's reputation as a champion of freedom and democracy on the global stage.
Against this backdrop of domestic discontent and international turmoil, the recent crisis in the Middle East served as a damning indictment of Bush's foreign policy legacy. The rush to military action in response to perceived threats had only exacerbated tensions and fueled instability in the region, with the specter of a global conflict looming ominously over the horizon. The crisis had laid bare the shortcomings of the administration's approach to diplomacy and crisis management, highlighting the need for a more nuanced and strategic approach to international relations. As the fallout from the crisis reverberated across the political landscape, Bush found himself grappling with the fallout of his foreign policy blunders. The debacle in the Middle East had become emblematic of the broader failures of his presidency, serving as a stark reminder of the high cost of reckless and unilateral action on the world stage. With his approval ratings at an all-time low and his presidency mired in controversy, Bush faced an uphill battle to salvage his legacy and restore public confidence in his leadership during the final years of his tenure.
Following the crisis that nearly sparked a global conflict, Russia emerged victorious in the battle of propaganda, particularly in the Global South, where public opinion shifted decisively in favor of Moscow over the West. The narrative propagated by Russian media outlets and diplomatic channels resonated deeply with many people in these regions, who viewed the United States as the primary instigator of the crisis and the greatest threat to global peace and stability. In the aftermath of the crisis, Moscow's strategic messaging portrayed Russia as a responsible actor committed to peace and dialogue, while casting the United States as an aggressive and destabilizing force willing to risk global catastrophe for its own interests. This narrative found fertile ground in the Global South, where historical grievances and suspicions of Western interventionism ran deep. The perception of Russia as a defender of sovereignty and a counterbalance to Western hegemony gained traction among many countries in the Global South, leading to a shift in geopolitical alignments and alliances. Russia's assertive stance in the crisis, coupled with its willingness to challenge Western narratives and assert its influence on the world stage, earned it newfound respect and admiration among nations seeking alternatives to Western dominance. Furthermore, China's growing influence and strategic partnership with Russia further bolstered Moscow's position in the Global South. As Beijing expanded its economic and diplomatic footprint across the region, it provided additional support for Russia's narrative of multipolarity and non-interference in the affairs of sovereign states. Together, Russia and China presented a compelling alternative to Western-centric approaches to global governance, resonating with countries seeking greater autonomy and agency in international affairs. The erosion of Western soft power in the Global South was palpable in the wake of the crisis, as trust and confidence in Western institutions and values waned in favor of alternative visions offered by Russia and China. The perceived arrogance and unilateralism of Western powers, exemplified by the crisis and its handling, further undermined their credibility and influence in regions traditionally viewed as their spheres of influence. As Russia and China capitalized on the opportunity to expand their influence in the Global South, Western powers faced a reckoning with the limits of their soft power and the consequences of their actions on the world stage. The crisis served as a wake-up call for Western policymakers, highlighting the urgent need to reassess their approach to diplomacy and engagement with the rest of the world in an increasingly multipolar and interconnected global landscape.
The near-miss of World War III in September 2007 had a profound impact on the global economy, exacerbating existing vulnerabilities and ultimately contributing to the onset of the Wall Street Crash in 2008. The specter of a global conflict, looming ominously over the horizon not once but twice within a few months, sent shockwaves through financial markets and investor confidence, triggering a chain reaction of economic instability and uncertainty. In the aftermath of the crisis, businesses and investors alike grappled with the heightened risk of geopolitical turmoil and its potential ramifications for trade, investment, and economic growth. The prospect of a major military confrontation involving world powers cast a pall of uncertainty over global markets, leading to heightened volatility and risk aversion among market participants. As tensions escalated and the brinkmanship between major powers intensified, businesses became increasingly cautious, delaying investment decisions and scaling back expansion plans in anticipation of potential disruptions to supply chains and market access. Trade flows were disrupted, as countries reevaluated their economic ties and sought to mitigate the risks posed by geopolitical instability. The threat of war also had a chilling effect on consumer confidence, as households braced for the possibility of rising costs, supply shortages, and broader economic dislocation in the event of a conflict. This cautious consumer sentiment translated into reduced spending and subdued demand across various sectors of the economy, further dampening growth prospects and exacerbating economic headwinds.
In the financial markets, the heightened geopolitical tensions fueled increased volatility and uncertainty, as investors grappled with the potential implications of a global conflict on asset prices and market dynamics. Stock markets experienced sharp swings in response to geopolitical developments, with risk-off sentiment dominating trading patterns and exacerbating sell-offs in equities and other risk assets. Moreover, the prospect of a major military confrontation raised concerns about the stability of key commodities markets, particularly oil and energy, as investors fretted over the potential disruption of critical supply routes and production facilities in conflict-prone regions. This uncertainty contributed to heightened price volatility in commodity markets, adding further pressure to already strained global economic conditions. As the crisis unfolded and diplomatic efforts to de-escalate tensions progressed, the global economy teetered on the brink of recession, with growth forecasts revised downward amid mounting uncertainty and fragility. The near-miss of World War III served as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of geopolitical events and economic outcomes, highlighting the need for effective crisis management and international cooperation to safeguard global stability and prosperity. Ultimately, the impact of the crisis on the world economy reverberated far beyond September 2007, laying the groundwork for the financial turmoil and economic downturn that culminated in the Wall Street Crash of 2008. The lessons learned from this tumultuous period underscored the importance of proactive risk management, robust crisis preparedness, and multilateral cooperation in navigating the complexities of an increasingly interconnected and uncertain global landscape.

(Military parade following entry of Transnistria to Union State in October 2007)
I
n October 2007, the geopolitical landscape witnessed a significant development as the citizens of the independent states of Transnistria and Gagauzia expressed their desire to join the Union of Belarus and Russia through referendums. These historic referendums marked a pivotal moment in the region's history, reflecting the aspirations of the people for closer ties with neighboring countries and a shared vision of political, economic, and security cooperation. Since the 1990s, both Transnistria and Gagauzia had maintained their status as independent states, internationally recognized entities, and strong allies of Moscow. Despite their independent status, they had long-standing cultural, historical, and linguistic connections with Russia, as well as deep-rooted ties to the broader Russian world. In Transnistria, a state with a predominantly Russian-speaking population, the referendum garnered overwhelming support for integration with the Union of Belarus and Russia. The outcome underscored the deep-seated historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between Transnistria and Russia, as well as the desire of its residents to strengthen these bonds through formal political union. Similarly, in Gagauzia, state inhabited predominantly by ethnic Gagauz people, the referendum yielded a resounding mandate for joining the Union of Belarus and Russia. The decision reflected the Gagauz people's affinity for the Russian world and their belief that closer integration with Belarus and Russia would bring about greater economic and financial opportunities. In response to the referendum results, the governments of Belarus and Russia welcomed Transnistria and Gagauzia into the Union with open arms, pledging to honor their commitments to uphold the rights and interests of their new constituents. Bilateral agreements were swiftly negotiated to facilitate the integration process, covering areas such as trade, defense cooperation, and cultural exchange. Des pite the challenges and complexities surrounding their integration into the Union of Belarus and Russia, the citizens of Transnistria and Gagauzia viewed the referendums as a historic opportunity to shape their own destiny and pursue a future aligned with their cultural and geopolitical affinities. The decision set the stage for a new chapter in the region's history, characterized by closer cooperation and collaboration between the Union and its newest members.
I
n November 2007, President Lukashenko embarked on a diplomatic tour to Africa, seizing the opportune moment to strengthen ties and explore avenues for cooperation between Russia and the nations of the African continent. This landmark tour marked a significant milestone in Russia's engagement with Africa, underscoring Moscow's commitment to expanding its influence and forging strategic partnerships beyond its traditional spheres of influence. With Russia's resurgence on the world stage and President Lukashenko's reputation as a formidable statesman, the timing was ripe for bolstering relations with African nations. The tour was meticulously planned to encompass a diverse array of countries, reflecting the strategic importance of Africa in Russia's geopolitical calculus and its desire to diversify its diplomatic and economic relationships. Throughout his journey, President Lukashenko engaged in high-level discussions with African leaders on a wide range of issues, including economic development, trade and investment, energy cooperation, security collaboration, and cultural exchange. These discussions were characterized by a spirit of mutual respect, cooperation, and shared aspirations for prosperity and development. Economic cooperation emerged as a central theme of the diplomatic tour, with President Lukashenko highlighting Russia's willingness to support African nations in their quest for sustainable growth and development.
Concrete proposals were put forward to enhance bilateral trade and investment, explore opportunities in key sectors such as energy, infrastructure, agriculture, and technology, and promote joint ventures and economic partnerships. Political dialogue also featured prominently during the tour, as President Lukashenko reaffirmed Russia's commitment to upholding the principles of sovereignty, non-interference, and mutual respect in its relations with African countries. The discussions focused on strengthening diplomatic ties, enhancing political dialogue, and fostering closer collaboration on regional and global issues of common concern. In addition to economic and political cooperation, military collaboration was another important aspect of President Lukashenko's agenda in Africa. Russia sought to expand its defense partnerships with African nations, offering training, equipment, and technical assistance to support their efforts in maintaining peace and security on the continent. Cultural diplomacy played a vital role in President Lukashenko's outreach to Africa, as he sought to deepen people-to-people ties and promote mutual understanding between Russia and African nations. Cultural exchanges, educational programs, and youth initiatives were explored as means of fostering greater interaction and cooperation between the two regions.
Overall, President Lukashenko's tour to Africa was met with enthusiasm and optimism by both Russian and African leadership, signaling a new chapter in their relationship characterized by partnership, solidarity, and mutual benefit. The tour laid the groundwork for enhanced cooperation and collaboration in the years to come, reaffirming Russia's commitment to playing a constructive and proactive role in Africa's development and prosperity.
President Lukashenko's landmark tour to Africa yielded a plethora of positive outcomes, leaving a lasting impact on Russia's engagement with the continent and laying the groundwork for enhanced cooperation across various domains. The tour was instrumental in deepening diplomatic ties, fostering economic partnerships, promoting cultural exchange, and strengthening Russia's presence and influence in Africa. One of the most significant outcomes of the tour was the consolidation of diplomatic relations between Russia and African nations. President Lukashenko's meetings with heads of state and government officials provided a platform for dialogue and cooperation on a wide range of bilateral and multilateral issues. Through constructive discussions and mutual engagement, trust and confidence were built, paving the way for closer diplomatic ties and collaboration on regional and global challenges. Economically, the tour resulted in the exploration of new avenues for trade and investment between Russia and Africa. President Lukashenko's discussions with African leaders identified opportunities for joint ventures, infrastructure projects, and economic partnerships that would benefit both sides. Agreements were reached to boost trade volumes, diversify economic activities, and promote sustainable development across the continent.

The tour also fostered enhanced cooperation in the energy sector, with discussions centered on leveraging Russia's expertise and resources to support Africa's energy needs. Collaborative efforts were initiated to develop renewable energy projects, expand access to electricity, and promote sustainable energy solutions that would contribute to Africa's economic growth and development. Furthermore, the tour served as a catalyst for greater cultural exchange and people-to-people ties between Russia and Africa. Cultural events, artistic performances, and educational programs were organized to showcase the rich cultural heritage of both regions and foster greater understanding and appreciation between their peoples. These initiatives contributed to building bridges of friendship and cooperation, fostering a sense of solidarity and mutual respect. From a geopolitical perspective, President Lukashenko's tour reaffirmed Russia's commitment to playing a constructive and proactive role in Africa's development and prosperity. By engaging with African nations on issues of mutual interest, Russia demonstrated its readiness to contribute to peace, stability, and sustainable development on the continent, while also advancing its own strategic objectives and interests. Overall, President Lukashenko's tour to Africa was hailed as a resounding success, heralding a new era of partnership, cooperation, and mutual benefit between Russia and Africa. The outcomes of the tour laid a solid foundation for future collaboration and engagement, opening up new opportunities for growth, prosperity, and shared progress for both regions.
President Lukashenko's tour in Africa marked a significant milestone in Russia's comprehensive entry onto the African continent, coinciding with a notable decline in Western influence and the emergence of China as a major player in Africa's economic and geopolitical landscape. The tour served as a catalyst for expanding Russia's footprint in Africa, capitalizing on the shifting dynamics of global power and the growing demand for alternative partnerships and investments. Amidst the decline of Western influence in Africa, characterized by waning economic dominance and diminishing political clout, Russia seized the opportunity to strengthen its ties with African nations and position itself as a key partner for the continent's development. President Lukashenko's diplomatic outreach and engagement with African leaders resonated with many nations seeking diversified partnerships and strategic alliances beyond traditional Western alliances.
The tour also underscored Russia's commitment to promoting a multipolar world order and challenging the dominance of Western powers in global affairs. By expanding its presence in Africa, Russia sought to counterbalance Western influence and assert its own interests and values on the international stage. This strategic maneuvering not only enhanced Russia's geopolitical standing but also contributed to the diversification of global power dynamics, fostering greater competition and cooperation among major powers. Furthermore, the decline of Western influence in Africa created a vacuum that was swiftly filled by China's growing presence and influence on the continent. As Western nations scaled back their engagement, China stepped up its investments, infrastructure projects, and diplomatic outreach in Africa, becoming Africa's largest trading partner and foreign investor. Russia's entry into Africa coincided with China's rise, presenting opportunities for collaboration and coordination between the two countries in pursuit of shared objectives and mutual interests. President Lukashenko's tour served to strengthen Russia's partnership with China in Africa, as both countries explored opportunities for joint initiatives and coordinated efforts to support Africa's development agenda. By aligning their strategies and leveraging their respective strengths, Russia and China aimed to enhance their influence and contribute to Africa's socio-economic progress, while also advancing their own strategic goals in the region. President Lukashenko's tour in Africa not only marked Russia's formal entry onto the continent but also signaled a broader shift in global power dynamics, with Russia and China emerging as prominent actors in Africa's evolving geopolitical landscape. The tour laid the groundwork for enhanced cooperation, economic engagement, and strategic collaboration between Russia, China, and African nations, reshaping the contours of international relations and shaping the future trajectory of Africa's development.

(In the wake of Western decline in Africa, Beijing had no intention of sharing the continent with Russia sparking competition between Moscow and Beijing)
Despite diplomatic overtures and rhetorical commitments, China swiftly moved to counter the resurgent presence of Russia on the African continent, signaling its unwillingness to share Africa with Russia in the wake of Western decline. This marked the beginning of a fierce battle between the resurgent Russia and China for dominance in the African market, as both global powers sought to expand their influence and secure access to the continent's abundant resources and emerging markets.
China's response to Russia's renewed engagement in Africa was characterized by a multifaceted strategy aimed at outmaneuvering Russian interests and consolidating its own position as the preeminent player on the continent. Beijing leveraged its economic prowess, investing heavily in infrastructure projects, natural resource extraction, and trade partnerships across Africa, thereby strengthening its ties with African governments and gaining a foothold in key sectors of the economy. Moreover, China employed diplomatic initiatives, engaging in high-level summits, bilateral meetings, and cultural exchanges to enhance its soft power and cultivate favorable relationships with African nations. Through these efforts, China sought to position itself as a reliable partner and benefactor, offering economic assistance, development aid, and technological expertise to address pressing challenges faced by African countries. Simultaneously, China pursued strategic objectives aimed at expanding its geopolitical influence and securing access to vital sea lanes and transportation routes in Africa. The construction of ports, railways, and energy infrastructure projects served not only to facilitate trade and commerce but also to bolster China's maritime capabilities and strategic presence in the region.
In response to China's assertive actions, Russia also embarked on a series of initiatives aimed at enhancing its presence and influence in Africa. Drawing on its historical ties and diplomatic relationships with African nations, resurgent Russia sought to reestablish itself as a key player on the continent, leveraging its economic resources, military capabilities, and diplomatic networks to advance its interests. One of the key pillars of Russia's strategy in Africa was the promotion of economic cooperation and investment. Moscow initiated a number of projects across various sectors, including energy, mining, infrastructure, and agriculture, aimed at tapping into Africa's vast natural resources and emerging markets. Russian companies entered into joint ventures and strategic partnerships with African counterparts, contributing to economic development and job creation in the region. Additionally, Russia sought to strengthen its military presence and security cooperation with African countries, offering training, equipment, and technical assistance to support their defense capabilities. Military cooperation agreements and arms sales agreements were forged, enabling African nations to enhance their defense capabilities and address security challenges more effectively. Diplomatically, Russia engaged in high-level dialogues and diplomatic exchanges with African leaders, seeking to build trust, foster cooperation, and address common challenges. Moscow hosted African heads of state and government, organized international forums and summits, and provided platforms for dialogue and exchange on issues of mutual interest.
Furthermore, Russia pursued cultural and educational exchanges, promoting people-to-people ties and fostering greater understanding and cooperation between Russia and Africa. Scholarships, academic programs, and cultural events were organized to strengthen cultural and educational links and promote cross-cultural dialogue and exchange. Despite these efforts, Russia faced stiff competition from China in Africa, as Beijing's vast economic resources, strategic investments, and diplomatic initiatives gave it an advantage. China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and its flagship Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) provided a comprehensive framework for engagement and cooperation, attracting widespread interest and participation from African countries. Moreover, China's flexible approach and willingness to adapt to local conditions and priorities resonated with African governments and communities, enabling Beijing to consolidate its position as Africa's leading trading partner and development partner. In light of China's growing influence and assertiveness in Africa, Russia faced the challenge of finding new avenues for engagement and differentiation. Moscow recognized the need to diversify its engagement strategies, enhance its value proposition, and strengthen its competitive advantage in key sectors. To this end, Russia sought to leverage its comparative advantages in areas such as defense, energy, and technology to carve out a niche for itself in the African market. Military cooperation, energy partnerships, and technological innovation emerged as areas of focus, where Russia could offer unique expertise and capabilities that complemented China's offerings. Furthermore, Russia emphasized the importance of building trust, fostering mutual respect, and promoting win-win cooperation in its relations with African partners. Moscow advocated for a multipolar world order based on equality, sovereignty, and non-interference, appealing to African nations' desire for greater autonomy and independence in their international relations. As Russia and China competed for influence in Africa, the continent emerged as a critical battleground for geopolitical supremacy and economic dominance. The outcome of this competition would not only shape the future trajectory of Africa's development but also have far-reaching implications for global power dynamics and the balance of power in the twenty-first century.
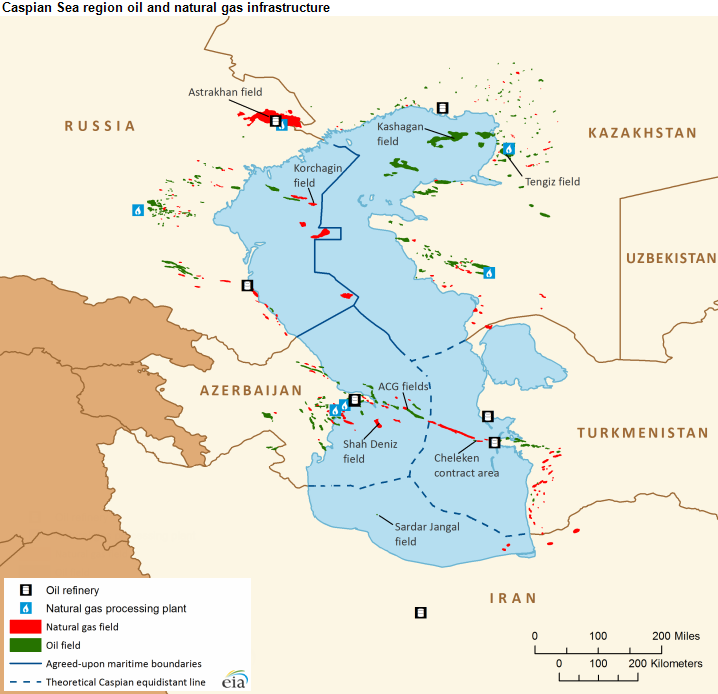
In December 2007, tensions flared in the Caspian Sea region as Russia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan became embroiled in a contentious tug of war over the status of the Caspian Sea. At the heart of the dispute lay the vast natural resources and mineral wealth believed to lie beneath the Caspian's waters, including oil, gas, and other lucrative commodities. The Caspian Sea, bordered by these five countries, holds significant strategic and economic importance due to its abundant energy reserves and its role as a key transit route for oil and gas exports. Control over the Caspian's resources has been a source of contention since the dissolution of the Soviet Union, as newly independent states sought to assert their territorial claims and secure access to the region's wealth. Russia, as the largest and most powerful state bordering the Caspian Sea, has historically maintained a dominant position in the region, leveraging its political influence and economic clout to advance its interests. Moscow has sought to uphold the principle of condominium, whereby all littoral states share sovereignty over the Caspian's resources, thereby preserving Russia's influence and ensuring its continued access to the region's energy wealth.
However, Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, and Turkmenistan have challenged Russia's hegemony in the Caspian, advocating for a division of the sea into distinct national sectors based on the equidistance principle, which would allocate each country a share of the sea's resources proportional to its coastline length. This approach would enable these countries to assert greater control over their respective maritime territories and exploit their natural resources independently of Russian dominance. The tug of war over the status of the Caspian Sea has been fueled by a combination of geopolitical rivalries, economic interests, and strategic calculations. Each littoral state has sought to maximize its share of the Caspian's resources while minimizing the influence of its neighbors and external powers. For Azerbaijan, the Caspian Sea represents a vital lifeline for its burgeoning oil and gas industry, providing access to lucrative energy reserves that are essential for its economic development and energy security. Baku has pushed for a fair and equitable division of the Caspian's resources, arguing that each littoral state should be entitled to a share of the sea's wealth commensurate with its geographical proximity and economic needs.
Iran, meanwhile, has asserted its historical claims to the Caspian, citing centuries-old treaties and agreements that recognize its sovereignty over certain parts of the sea. Tehran has resisted attempts to divide the Caspian into national sectors, insisting on a condominium arrangement that preserves Iran's rights and ensures its participation in the management of the region's resources. Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan, as emerging energy powers in the Caspian basin, have sought to assert their sovereignty over their respective maritime territories and secure control over the resources located therein. Astana and Ashgabat have pursued bilateral agreements with other littoral states to delineate their maritime boundaries and clarify their rights to exploit the Caspian's resources. Amidst this complex geopolitical landscape, tensions have periodically escalated between the Caspian littoral states, as competing claims and overlapping interests have fueled disputes and diplomatic wrangling. Negotiations over the legal status of the Caspian Sea have been ongoing for decades, with intermittent progress made towards reaching a comprehensive agreement that addresses the concerns of all parties involved. The outcome of the tug of war over the Caspian Sea will have far-reaching implications for regional stability, energy security, and geopolitical dynamics in Eurasia.
In December 2007, the geopolitical landscape of Eurasia witnessed a significant development as Pakistan, a close ally of China, and India, a key partner of Russia, both joined the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO). This move marked a crucial juncture in the delicate game of balance between Russia and China within the SCO and the broader Eurasian region. The SCO, originally founded by China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan, aimed to enhance regional cooperation on security, economic, and cultural issues. With the inclusion of Pakistan and India, the SCO expanded its membership to include two major South Asian powers, further solidifying its role as a significant player in regional affairs. For China, Pakistan's accession to the SCO represented a strategic victory, strengthening Beijing's influence in South Asia and providing a platform for closer cooperation with Islamabad on issues of mutual interest. Pakistan, in turn, viewed its membership in the SCO as an opportunity to deepen its ties with China and enhance its strategic position vis-à-vis India. On the other hand, India's decision to join the SCO signaled its desire to engage more actively in regional cooperation and address common challenges alongside its neighbors. For Russia, India's accession to the SCO offered an opportunity to bolster its strategic partnership with New Delhi and counterbalance China's growing influence within the organization. The inclusion of Pakistan and India in the SCO injected new dynamics into the organization, as the delicate balance of power between Russia and China became increasingly apparent.
Both Moscow and Beijing sought to leverage their respective partnerships with Islamabad and New Delhi to advance their strategic objectives within the SCO and shape its agenda to align with their interests. At the same time, the SCO provided a forum for constructive engagement and dialogue among its members, offering a platform for resolving regional disputes and promoting stability and development across Eurasia. As Pakistan and India navigated their roles within the organization, they faced the challenge of balancing their competing interests while seeking to contribute positively to the SCO's objectives. The delicate game of balance between Russia and China within the SCO reflected broader geopolitical trends in Eurasia, where competing interests and strategic calculations intersected with efforts to foster cooperation and mutual understanding. As Pakistan and India settled into their roles as full members of the SCO, they would play a crucial role in shaping the organization's future trajectory and influencing regional dynamics in South Asia and beyond. For Russia and China, the inclusion of Pakistan and India in the SCO presented both opportunities and challenges. While the expanded membership strengthened the organization's regional footprint and enhanced its relevance on the global stage, it also introduced new complexities and considerations into the dynamics between Moscow and Beijing. As the SCO continued to evolve, navigating these complexities would require skillful diplomacy, pragmatic cooperation, and a shared commitment to advancing the common interests of all member states.

In January 2008, the world witnessed a historic moment in the realm of international finance as the Russian National Wealth Fund (NWF) achieved the remarkable feat of becoming the largest sovereign wealth fund on the planet. This achievement, which saw the Russian fund surpassing the esteemed Government Pension Fund of Norway in terms of assets under management, marked a watershed moment not only for Russia but also for the broader global financial landscape. The genesis of the Russian National Wealth Fund dates back to the late 1990s, a period marked by significant economic reforms and restructuring efforts in Russia following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Recognizing the immense potential of the country's abundant natural resource wealth, particularly its vast reserves of oil and gas, Russian policymakers conceived the idea of establishing a sovereign wealth fund to safeguard the nation's economic stability and provide for future generations. Over the ensuing years, the Russian NWF underwent a process of steady growth and expansion, buoyed by prudent fiscal management and strategic investment decisions. With a mandate to preserve and grow the nation's wealth, the fund diversified its portfolio across a spectrum of asset classes, including equities, fixed income securities, real estate, and alternative investments. This diversified approach not only helped to optimize returns but also served to mitigate risks and enhance the fund's resilience in the face of market volatility.
By January 2008, the Russian National Wealth Fund had matured into a formidable financial powerhouse, boasting assets that eclipsed those of its counterparts around the world. Its meteoric rise to the top of the sovereign wealth fund rankings underscored Russia's emergence as a major player in the global economy, commanding attention and respect on the world stage. The significance of the Russian NWF's achievement extended far beyond mere numbers. It symbolized Russia's transition from a nation in economic transition to a powerhouse of global finance, capable of shaping investment trends, driving economic growth, and influencing market dynamics on a global scale. With its newfound status as the world's largest sovereign wealth fund, Russia had firmly established itself as a force to be reckoned with in the realm of international finance. Moreover, the Russian National Wealth Fund's ascent to the top of the rankings signaled Russia's commitment to responsible resource management and prudent fiscal stewardship. As custodians of the nation's wealth, Russian policymakers recognized the importance of ensuring the long-term prosperity and stability of the country, leveraging the fund's resources to support economic and social development of Russia and the Russian people.
In the annals of global finance and technology, the year 2008 marked a pivotal moment with the meteoric rise of DST Global and its enigmatic founder, Yuri Milner. As the world grappled with the fallout of the financial crisis, DST Global emerged as a beacon of innovation and opportunity, reshaping the landscape of venture capital and investment in the digital age. Founded by Yuri Milner, a Russian entrepreneur and former physicist, DST Global quickly captured the imagination of investors and industry insiders with its bold vision and ambitious investment strategy. Under Milner's leadership, DST Global pioneered a new model of venture capital investing, leveraging data-driven insights and strategic partnerships to identify and capitalize on emerging trends in technology and innovation. At the heart of DST Global's success was Milner's unique blend of scientific acumen, entrepreneurial spirit, and keen strategic foresight. With a background in theoretical physics and a deep understanding of complex systems, Milner brought a rigorous analytical approach to the world of finance, revolutionizing the way investments were made and evaluated. One of DST Global's most notable achievements was its early bet on social media giant Facebook, a move that would prove to be one of the most lucrative investments in the history of venture capital. By recognizing the transformative potential of social networking and technology platforms, DST Global positioned itself at the forefront of the digital revolution, paving the way for unprecedented growth and innovation in the years to come.
But DST Global's influence extended far beyond Silicon Valley, as Milner and his team embarked on a global quest to identify and support the most promising startups and entrepreneurs across the world. From e-commerce and fintech to biotech and artificial intelligence, DST Global's diverse portfolio spanned a wide range of industries and sectors, reflecting Milner's belief in the power of technology to drive positive change and create value on a global scale. Yet, amidst its meteoric rise, DST Global also faced scrutiny and speculation about its ties to the Kremlin and the Russian government. As rumors swirled about the source of its funding and the nature of its relationship with Russian oligarchs and state-owned enterprises, Milner found himself thrust into the spotlight as a figure of intrigue and controversy in the world of finance and geopolitics. Despite the rumors and innuendo, Milner remained steadfast in his commitment to innovation and progress, guiding DST Global through turbulent waters with unwavering confidence and determination. As the firm continued to expand its reach and influence, Milner's reputation as a visionary investor and trailblazing entrepreneur grew, solidifying DST Global's status as a major player in the global investment landscape.
Amidst the meteoric rise of DST Global and Yuri Milner in 2008, whispers and speculations emerged regarding the firm's ties to the Kremlin, casting a shadow of intrigue and controversy over its burgeoning success. Allegations swirled suggesting that DST Global, despite its outward appearance as an independent investment powerhouse, was indirectly managed by the Kremlin, serving as a conduit for Russian state interests in the global technology sector. One of the most compelling pieces of evidence supporting these claims surfaced in the form of financial transactions involving Kremlin-linked entities and DST Global. It was revealed that VTB Bank, a Russian financial institution with close ties to the Kremlin, injected a staggering $300 million into DST Global. This substantial infusion of capital provided by VTB Bank raised eyebrows and fueled suspicions about the true nature of DST Global's funding and its relationship with the Russian government. Further scrutiny of DST Global's investment activities uncovered a web of interconnected deals involving Kremlin-controlled entities and strategic investments in prominent technology companies. For instance, it was disclosed that a subsidiary of Gazprom, the state-owned Russian energy giant, had funded an investment company that collaborated with DST Global to acquire shares in Facebook, the social media behemoth. This partnership proved to be immensely profitable, with DST Global and its Kremlin-linked associates reaping substantial returns when Facebook went public, further fueling speculation about the firm's ties to the Russian government.
The revelation of these financial arrangements between DST Global and Kremlin-affiliated entities sent shockwaves through the global investment community, prompting questions about the extent of Russian state influence in the burgeoning technology sector. Critics and observers raised concerns about the potential implications of Kremlin involvement in Silicon Valley, fearing that it could undermine the integrity of the technology industry and compromise the autonomy of innovative startups and entrepreneurs. Amidst mounting scrutiny and public scrutiny, Yuri Milner and DST Global found themselves thrust into the center of a geopolitical firestorm, grappling with allegations of Kremlin influence and questions about the firm's independence and integrity. While Milner vehemently denied any direct ties to the Russian government, the revelations surrounding DST Global's financial dealings with Kremlin-linked entities raised serious doubts about the true nature of the firm's operations and its commitment to transparency and accountability.

(15 March 2008 would later be considered a day, when American unipolar domination over the World ended)
The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers, also known as the Crash of '08 on March 15, 2008, was the climax of the subprime mortgage crisis. After the financial services firm was notified of a pending credit downgrade due to its heavy position in subprime mortgages, the Federal Reserve summoned several banks to negotiate financing for its reorganization. These discussions failed, and Lehman filed a Chapter 11 petition that remains the largest bankruptcy filing in U.S. history, involving more than US$600 billion in assets. The bankruptcy triggered a 6.5% one-day drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average, then the largest decline since the attacks of September 11, 2001. It signaled a limit to the government's ability to manage the crisis and prompted a general financial panic. Money market mutual funds, a key source of credit, saw mass withdrawal demands to avoid losses, and the interbank lending market tightened, threatening banks with imminent failure. The government and the Federal Reserve system responded with several emergency measures to contain the panic. Lehman Brothers was one of the first Wall Street firms to move into the business of mortgage origination. In 1997, Lehman bought Colorado-based lender Aurora Loan Services, an Alt-A lender. In 2000, to expand their mortgage origination pipeline, Lehman purchased West Coast subprime mortgage lender BNC Mortgage LLC. Lehman quickly became a force in the subprime market. By 2003 Lehman made $18.2 billion in loans and ranked third in lending. By 2004, this number topped $40 billion. By 2006, Aurora and BNC were lending almost $50 billion per month.
Lehman had morphed into a real estate hedge fund disguised as an investment bank. By 2008, Lehman had assets of $680 billion supported by only $22.5 billion of firm capital. From an equity position, its risky commercial real estate holdings were thirty times greater than capital. In such a highly leveraged structure, a three- to five-percent decline in real estate values would wipe out all capital. Lehman borrowed significant amounts to fund its investing in the years leading to its bankruptcy in 2008, a process known as leveraging or gearing. A significant portion of this investment was in housing-related assets, making it vulnerable to a downturn in that market. One measure of this risk-taking was its leverage ratio, a measure of the ratio of assets to owners equity, which increased from approximately 24:1 in 2003 to 31:1 by 2007. While generating tremendous profits during the boom, this vulnerable position meant that just a 3–4% decline in the value of its assets would entirely eliminate its book value of equity. Investment banks such as Lehman were not subject to the same regulations applied to depository banks to restrict their risk-taking.
In August 2007, Lehman closed its subprime lender, BNC Mortgage, eliminating 1,200 positions in 23 locations, and took a $25-million after-tax charge and a $27-million reduction in goodwill. The firm said that poor market conditions in the mortgage space "necessitated a substantial reduction in its resources and capacity in the subprime space". In 2008, Lehman faced an unprecedented loss due to the continuing subprime mortgage crisis. Lehman's loss resulted from having held onto large positions in subprime and other lower-rated mortgage tranches when securitizing the underlying mortgages. Whether Lehman did this because it was simply unable to sell the lower-rated bonds or made a conscious decision to hold them is unclear. In any event, huge losses accrued in lower-rated mortgage-backed securities throughout 2008. In the second fiscal quarter, Lehman reported losses of $2.8 billion and decided to raise $6 billion in additional capital by offering new shares. In period between October 2007 to January 2008 alone, Lehman stock lost 73% of its value as the credit market continued to tighten.In February 2008, Lehman reported that it intended to lay-off 6% of its work force, 1,500 people, just ahead of its first-quarter-reporting deadline in March. On February 22, shares in Lehman closed up 5% (16% for the week) on reports that the state-controlled Korea Development Bank was considering buying Lehman. Most of those gains were quickly eroded as news emerged that Korea Development Bank was "facing difficulties pleasing regulators and attracting partners for the deal." It culminated on March 9, when Lehman's shares plunged 45% to $7.79, after it was reported that the state-run South Korean firm had put talks on hold.
Investor confidence continued to erode as Lehman's stock lost roughly half its value and pushed the S&P 500 down 3.4% on March 9. The Dow Jones lost nearly 300 points the same day, on investors' concerns about the security of the bank. The U.S. government did not announce any plans to assist with any possible financial crisis that emerged at Lehman. On March 10, Lehman announced a loss of $3.9 billion and their intent to sell off a majority stake in their investment-management business, which included Neuberger Berman. The stock slid 7% that day. On March 12, Timothy F. Geithner, then president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, called a meeting on the future of Lehman, which included the possibility of an emergency liquidation of its assets. Bankers representing all the major Wall Street firms were in attendance. The meeting goal was to find a private solution in rescuing Lehman and extinguish the flame of the global financial crisis. Lehman reported that it had been in talks with Bank of America and Barclays for the company's possible sale. The New York Times reported on March 14, 2008, that Barclays had ended its bid to purchase all or part of Lehman and a deal to rescue the bank from liquidation collapsed. It emerged subsequently that a deal had been vetoed by the Bank of England and the UK's Financial Services Authority. Leaders of major Wall Street banks continued to meet late that day to prevent the bank's rapid failure. Bank of America's rumored involvement also appeared to end as federal regulators resisted its request for government involvement in Lehman's sale. By Sunday, March 14, after the Barclays deal fell through, the news of impending doom swept through Lehman, and many employees arrived at the headquarters to clean out their offices. By Sunday afternoon, the government summoned Harvey Miller of Weil, Gotshal & Manges to file for bankruptcy before the markets opened on Monday.


